Mobile:+86-311-808-126-83
Email:info@ydcastings.com
Understanding the Differences Between Forging and Casting Techniques in Metalworking
Forging and Casting Understanding Two Key Metalworking Processes
Forging and Casting Understanding Two Key Metalworking Processes
Forging is a manufacturing process that involves the shaping of metal using localized compressive forces. This is typically done by hammering, pressing, or rolling the metal at high temperatures, which enhances its malleability. The heat and pressure cause the metal to deform, allowing it to be formed into specific shapes such as bars, sheets, or intricate components. The result is a product that is often stronger and more durable than those produced through other methods. When metals are forged, their internal grain structure is refined, leading to improved mechanical properties such as tensile strength and fatigue resistance. Forging is commonly used in the production of tools, hardware, automotive parts, and various machinery components.
what is forging and casting
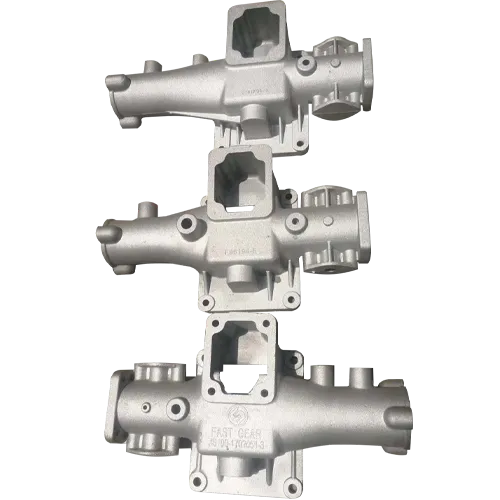
In contrast, casting is a process where molten metal is poured into a mold and allowed to solidify. This method is ideal for producing complex shapes and large components that may be difficult or impossible to create through forging. Casting can be performed using a variety of metals and alloys, including iron, aluminum, copper, and steel. Once the metal cools and solidifies, the mold is removed to reveal the cast piece. While casting allows for intricate designs and shapes, it may produce products with lower mechanical properties compared to forged items. However, advancements in casting techniques, such as investment casting and precision casting, have significantly improved the quality and strength of casted components, making them suitable for diverse applications, from decorative elements to critical engine parts.
Another notable difference between the two processes is their energy consumption and production costs. Forging generally requires a significant amount of energy due to the high temperatures and forces involved, while casting can be more energy-efficient, especially for mass production. Nonetheless, casting may involve higher labor costs due to mold preparation and finishing processes.
In summary, forging and casting are two essential metalworking processes with distinct characteristics. Forging offers enhanced strength and durability, making it ideal for high-performance applications, while casting provides versatility in shape and design, catering to a wide range of industries. Understanding these processes allows manufacturers to select the appropriate method based on the requirements of their specific projects, ultimately leading to better product quality and performance.
-
Why Should You Invest in Superior Pump Castings for Your Equipment?NewsJun.09,2025
-
Unlock Performance Potential with Stainless Impellers and Aluminum End CapsNewsJun.09,2025
-
Revolutionize Your Machinery with Superior Cast Iron and Aluminum ComponentsNewsJun.09,2025
-
Revolutionize Fluid Dynamics with Premium Pump ComponentsNewsJun.09,2025
-
Optimizing Industrial Systems with Essential Valve ComponentsNewsJun.09,2025
-
Elevate Grid Efficiency with High-Precision Power CastingsNewsJun.09,2025











