Mobile:+86-311-808-126-83
Email:info@ydcastings.com
English
Precision Stainless Steel Investment Casting | Durable, Complex Parts
Introduction to Stainless Steel Investment Casting
Precision engineering in critical industrial applications demands components with superior material integrity, intricate geometries, and exceptional surface finish. This is precisely where stainless steel investment casting excels. Also known as lost-wax casting, this advanced manufacturing process is paramount for producing high-tolerance parts for diverse sectors, from aerospace to medical devices. Its ability to create near-net-shape components reduces subsequent machining, saving both time and cost while ensuring the metallurgical properties required for demanding environments. This article delves into the intricacies of this robust process, exploring its technical advantages, application potential, and the strategic considerations for procurement and partnership.
The demand for parts that can withstand extreme temperatures, corrosive agents, and high mechanical stresses continues to grow, making stainless steel alloys an ideal material choice. When combined with the precision of investment casting, the result is components that offer unparalleled performance and reliability.
Industry Trends and Market Dynamics
The global market for precision casting, particularly involving advanced alloys, is witnessing substantial growth, driven by an increasing emphasis on energy efficiency, environmental regulations, and automation. Key trends include the miniaturization of components, the demand for complex internal passages, and the integration of smart manufacturing principles. Industries are increasingly seeking suppliers capable of delivering high-quality, repeatable, and cost-effective solutions. The shift towards higher performance materials and tighter tolerances means that traditional casting methods, such as green sand metal casting, are often being supplemented or replaced by more sophisticated processes like stainless investment casting. This evolution is also fueling innovation in alloy development, where specific grades of stainless steel are engineered for enhanced properties tailored to specific industrial challenges.
Furthermore, the rise of Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT) is pushing manufacturers to adopt advanced monitoring and control systems within the casting process itself, ensuring greater consistency and reduced defects. This technological integration is vital for maintaining competitiveness and meeting stringent quality requirements from end-users.
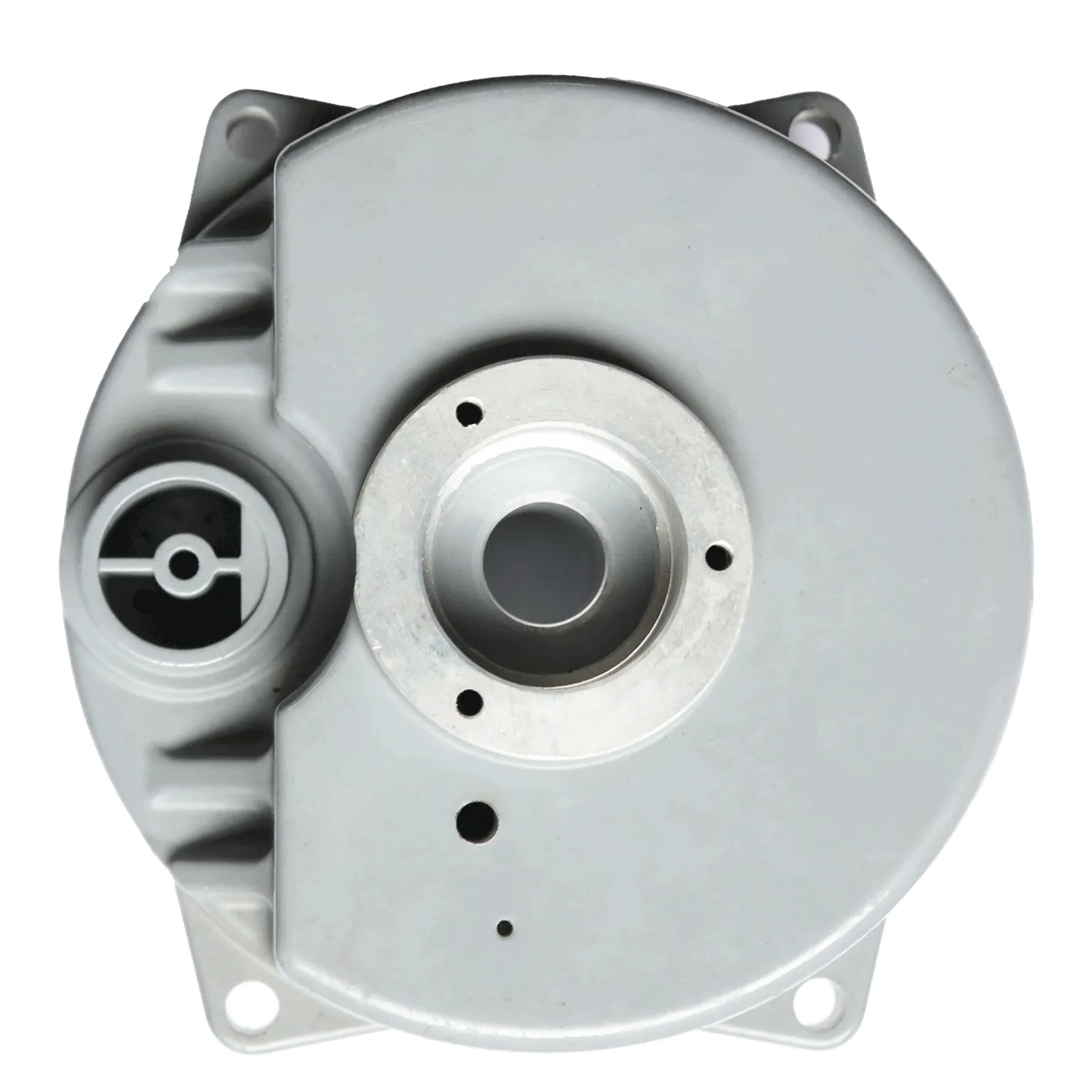
Detailed Process Flow of Stainless Steel Investment Casting
Overview of Manufacturing Stages and Materials
The stainless steel investment casting process is a multi-step methodology renowned for its precision and ability to produce complex components with minimal post-processing.
- Wax Pattern Creation: An aluminum master die is used to inject molten wax, creating a precise replica of the final part. Multiple wax patterns are then assembled onto a central wax sprue, forming a "tree."
- Slurry and Stucco Coating: The wax tree is repeatedly dipped into a ceramic slurry (typically silica-based, often with colloidal silica binders) and then coated with refractory stucco material (e.g., zircon sand, fused silica). This multi-layer process builds a robust ceramic shell around the wax pattern.
- Dewaxing: The ceramic shell is heated in an autoclave, melting and removing the wax. The wax can often be reclaimed and reused, reducing waste.
- Shell Firing: The ceramic shell is fired at high temperatures (typically 900-1150°C) to burn out residual wax, strengthen the shell, and remove moisture, preparing it for molten metal.
- Metal Pouring: Molten stainless steel, often specific grades like 304, 316, 17-4 PH, or duplex stainless steels, is poured into the preheated ceramic molds. The preheating helps ensure complete filling and prevents thermal shock. The melting process typically occurs in induction furnaces to maintain precise temperature and alloy composition.
- Cooling and Solidification: The metal cools and solidifies within the ceramic mold, taking the shape of the original wax patterns.
- Shell Removal: The ceramic shell is broken off using vibratory hammers, water blasting, or other mechanical means to reveal the cast metal parts.
- Finishing Operations: The individual castings are separated from the sprue, gates are removed, and subsequent finishing includes grinding, sandblasting, heat treatment (e.g., annealing, solution treatment for specific stainless grades), and potentially CNC machining for critical features.
- Quality Inspection: Each part undergoes rigorous inspection, including visual checks, dimensional verification, non-destructive testing (NDT) like X-ray, magnetic particle, or liquid penetrant inspection, and destructive testing (DT) for mechanical properties verification.
Materials and Specifications
Materials commonly processed via stainless steel investment casting include:
- Austenitic Stainless Steels: 304, 304L, 316, 316L, 310, 321. Known for excellent corrosion resistance, ductility, and good weldability. Widely used in chemical, food processing, and medical industries.
- Martensitic Stainless Steels: 410, 420, 440C. Offer high strength and hardness but lower corrosion resistance than austenitic grades. Applications include cutlery, surgical instruments, and turbine blades.
- Duplex Stainless Steels: 2205, 2507. Combine properties of austenitic and ferritic steels, offering superior strength and corrosion resistance (especially stress corrosion cracking). Ideal for petrochemical, offshore, and marine applications.
- Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steels: 17-4 PH (630). Extremely high strength and hardness, good corrosion resistance. Used in aerospace, nuclear, and high-performance valve components.
Testing standards typically adhere to ISO (International Organization for Standardization) series, such as ISO 9001 for quality management, and material-specific standards like ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) and ANSI (American National Standards Institute) for chemical composition, mechanical properties, and non-destructive examination. Many components must also comply with industry-specific standards, such as those from the API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas, or FDA (Food and Drug Administration) regulations for medical devices.
The typical service life of these components can range from decades in static, less aggressive environments to several years in highly corrosive or high-stress applications, depending on the alloy selection, design, and operating conditions. For example, a 316L stainless investment casting valve body in a clean water system might last 50+ years, while the same alloy in a highly acidic chemical process might have a shorter, though still extensive, lifespan.

Technical Specifications and Advantages
Key Parameters and Performance Metrics
The inherent capabilities of stainless steel investment casting offer significant advantages over alternative manufacturing methods like forging or fabrication.
- Design Freedom: Enables production of complex, intricate geometries, thin walls, and internal passageways that are difficult or impossible to achieve with other methods.
- Superior Surface Finish: Typically, Ra 3.2-6.3 µm (125-250 micro-inches), significantly reducing or eliminating the need for additional surface finishing processes.
- Tight Dimensional Tolerances: Standard linear tolerances typically range from ±0.005 in/in (±0.127 mm/25.4 mm) for the first inch, and ±0.003 in/in (±0.076 mm/25.4 mm) thereafter. For critical dimensions, even tighter tolerances can be achieved.
- Material Versatility: Accommodates a vast array of stainless steel alloys, allowing for optimization of mechanical and chemical properties for specific applications.
- Metallurgical Integrity: Creates components with uniform grain structure and density, free from porosity and internal defects, leading to enhanced mechanical strength and fatigue resistance.
- Cost-Effectiveness: For complex parts, investment casting can be more economical than machining from billet or extensive fabrication, especially in medium to high production volumes, due to reduced material waste and minimal secondary operations.
Product Specification Table: Typical Stainless Steel Investment Casting (Cover)
Application Scenarios and Target Industries
The versatility and high performance of components produced through stainless steel investment casting make them indispensable across a wide array of demanding industries.
- Petrochemical and Oil & Gas: Valve bodies, pump housings, impellers, and fittings that require extreme corrosion resistance and high-pressure integrity. The ability to cast complex internal geometries is crucial for flow efficiency, contributing to energy saving.
- Metallurgy and Heavy Industry: Components for high-temperature furnaces, wear-resistant parts, and structural elements exposed to harsh chemical environments.
- Water Supply & Drainage: Critical parts for water treatment plants, municipal pumping stations, and desalination facilities, where corrosion resistance against chlorinated water or seawater is paramount.
- Food & Beverage Processing: Hygienic fittings, nozzles, and machine parts that require smooth surface finishes and non-corrosive properties to meet strict sanitation standards (e.g., FDA compliance).
- Medical and Pharmaceutical: Surgical instruments, prosthetic components, and drug delivery device parts, benefiting from biocompatibility and intricate designs.
- Automotive and Aerospace: Turbocharger components, structural brackets, and specialized engine parts where strength-to-weight ratio and heat resistance are critical.
In a typical application scenario, consider a pump impeller used in a chemical processing plant. Machining this complex, multi-vaned component from a solid billet would be prohibitively expensive and wasteful. Forging might simplify some aspects but would still require extensive post-machining. However, with stainless investment casting, the impeller can be cast near-net-shape using a duplex stainless steel (e.g., 2205) for superior corrosion resistance against aggressive chemicals, while maintaining precise aerodynamic profiles for optimal energy efficiency. This demonstrates both the corrosion resistance and energy saving advantages inherent to the process.

Vendor Comparison: Investment Casting vs. Other Methods
When evaluating manufacturing methods for metal components, decision-makers often weigh the pros and cons of investment casting against alternatives such as sand casting, forging, and CNC machining.
Comparison Table: Casting Methods
Choosing a casting partner requires meticulous due diligence. Look for certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100 for aerospace), extensive experience (years of service, specific alloy expertise), and a proven track record of successful client projects. A robust quality control system, including in-house material testing and NDT capabilities, is crucial. Additionally, consider their ability to provide comprehensive customized solutions, from design support to final inspection and logistics.
Customized Solutions and Case Studies
Tailored Approaches for Unique Requirements
Modern manufacturing demands more than just standard parts; it requires tailored solutions. A proficient stainless investment casting provider offers comprehensive customization, beginning with collaborative design for manufacturability (DFM) support. This involves optimizing component design for the casting process to achieve desired performance, reduce material usage, and minimize secondary operations. Services typically include:
- 3D Modeling & Simulation: Advanced CAD/CAE tools for pattern design, mold flow analysis, and solidification simulation to predict and prevent defects.
- Alloy Selection Expertise: Guiding clients in choosing the optimal stainless steel grade, or even specific aluminium alloy for casting if that route is more suitable, based on environmental conditions, mechanical stresses, and cost considerations.
- Post-Casting Treatments: Custom heat treatments, surface finishes (e.g., electropolishing, passivation), and precision CNC machining for features requiring extremely tight tolerances.
- Assembly and Sub-Assembly: Providing value-added services by combining cast components with other manufactured parts into complete sub-assemblies.
Application Case Study: High-Pressure Valve Components
A leading oil and gas firm required highly specialized valve components for deep-sea applications, demanding exceptional corrosion resistance against brine and hydrogen sulfide, coupled with integrity under pressures up to 15,000 PSI. Traditional metal casting near me solutions using sand casting failed to meet the stringent surface finish and dimensional accuracy needed, leading to costly leaks and premature failures.
Our solution involved leveraging stainless steel investment casting with a specific super duplex stainless steel alloy (e.g., UNS S32760). Through advanced simulation, the wax pattern and gating system were optimized to ensure uniform solidification, minimizing porosity and internal stresses. The as-cast components achieved an Ra 3.2 µm surface finish, drastically reducing cavitation potential and improving flow characteristics. Post-casting, solution annealing was performed to optimize mechanical properties, followed by precision CNC machining on critical sealing surfaces. Non-destructive testing, including X-ray and ultrasonic inspection, confirmed zero internal defects.
The client reported a 30% reduction in overall lead time compared to previous methods, an estimated 15% cost saving due to reduced machining, and a significant improvement in the service life and reliability of their subsea valve assemblies, exceeding performance metrics by over 20%. This success highlights the power of specialized stainless investment casting solutions in meeting extreme engineering challenges.
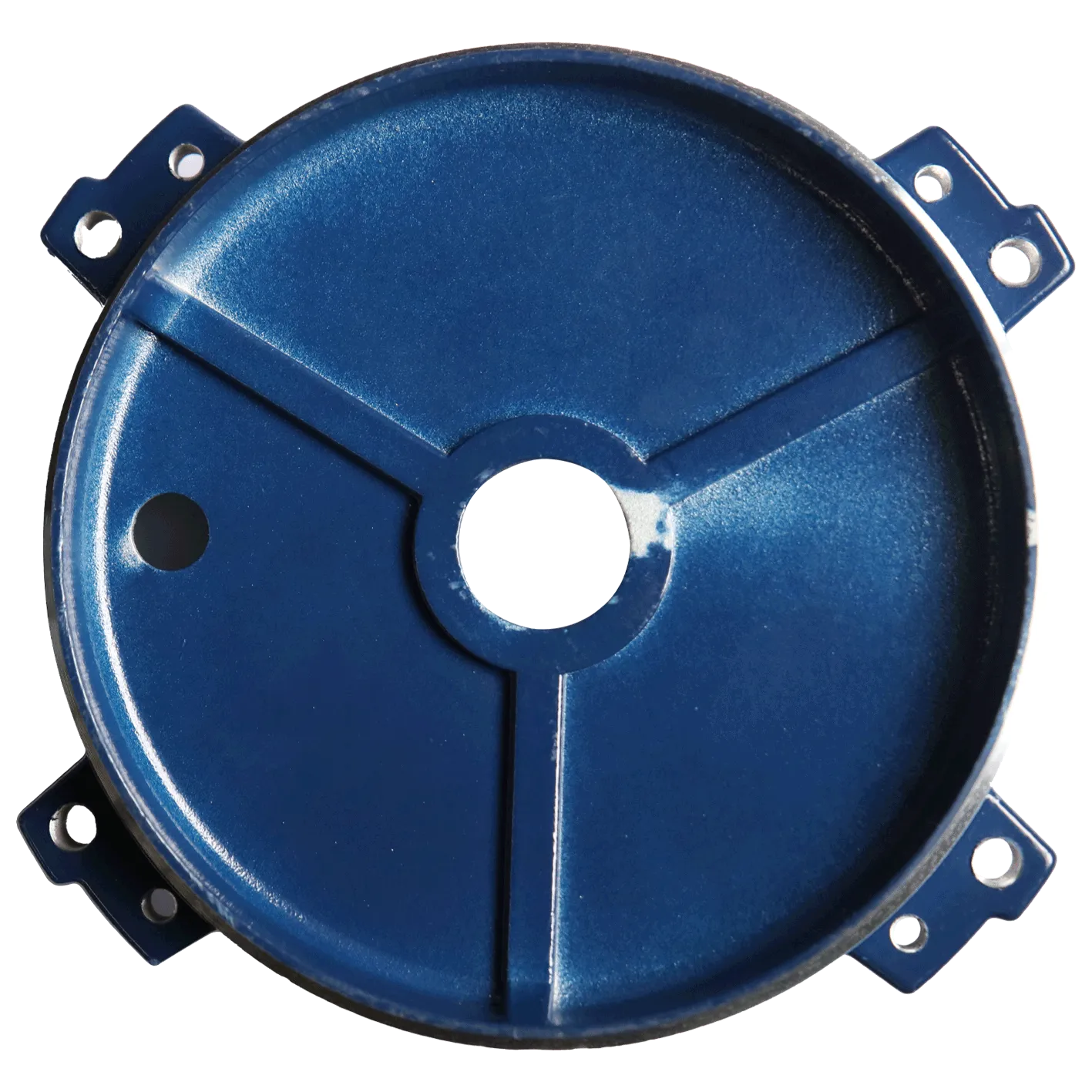
Trustworthiness and Support
Building trust in B2B partnerships is paramount. Our commitment to transparency, quality, and customer satisfaction is reflected in our robust support infrastructure. We hold certifications such as ISO 9001:2015, demonstrating our adherence to globally recognized quality management standards, and our facility undergoes regular audits to ensure compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: What is the typical lead time for stainless steel investment casting?
A: Lead times vary significantly based on complexity, quantity, and specific alloy. For new tooling and initial samples, it can range from 6-12 weeks. Production runs typically range from 4-8 weeks after sample approval. We offer expedited services for urgent requirements. - Q: What are your minimum order quantities (MOQ)?
A: MOQs are flexible and depend on part size and complexity. We work with clients on both small-batch prototyping and high-volume production. Please contact us with your specific needs for a tailored quote. - Q: What kind of warranty do you offer on your castings?
A: We provide a comprehensive warranty against manufacturing defects in material and workmanship, typically for one year from the date of shipment. Specific terms are outlined in our supply agreements and adhere to industry standards. Our goal is 100% customer satisfaction. - Q: Can you assist with material selection and design optimization?
A: Absolutely. Our experienced engineering team offers extensive DFM support, assisting with alloy selection, optimizing geometry for castability, and recommending post-processing for optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Lead Time and Fulfillment
Our integrated project management approach ensures clear communication and streamlined execution. We provide detailed production schedules, from tooling fabrication to final inspection and shipment. Fulfillment options include flexible logistics, global shipping capabilities, and inventory management programs to support just-in-time (JIT) deliveries for long-term partners.
Warranty and After-Sales Support
Beyond our product warranty, our commitment extends to comprehensive after-sales support. This includes technical assistance, troubleshooting, and continuous improvement initiatives based on field performance data. Our dedicated customer service team is available to address any inquiries or concerns promptly, ensuring sustained operational excellence for our clients.
Conclusion
Stainless steel investment casting stands as a pinnacle of precision manufacturing, offering unparalleled capabilities for creating complex, high-performance components. Its distinct advantages in design freedom, surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and material integrity make it the preferred choice for critical applications across numerous industries. By partnering with a reputable and experienced casting provider, businesses can unlock significant value, optimize their supply chains, and ensure the long-term reliability of their most vital equipment. The continuous evolution of this technology, coupled with advanced engineering expertise, ensures its continued relevance and growth in the global industrial landscape.
References
- ASM Handbook, Volume 15: Casting. ASM International, 2008.
- Campbell, J. Complete Casting Handbook: Metal Casting Processes, Metallurgy, Techniques and Design. Butterworth-Heinemann, 2011.
- ASTM International Standards for Stainless Steel Castings.
- ISO 9001:2015 Quality management systems – Requirements.
-
Materials Used in Manufacturing Cap End Pipe FittingsNewsNov.24,2025
-
Material Properties of CF8M CastingNewsNov.24,2025
-
How to Inspect Pump Cap Ends for DamageNewsNov.21,2025
-
Backward Curved Impeller – Efficient Airflow Solutions for Industry | YD CastingsNewsNov.21,2025
-
Automobile Water Pump - Efficient, Quiet, Durable & ElectricNewsNov.21,2025
-
Impeller for Pumps – High-Efficiency, Durable, OEM-ReadyNewsNov.21,2025











