Mobile:+86-311-808-126-83
Email:info@ydcastings.com
Sand & Continuous Casting Process Guide Efficient Metal Solutions
- Foundational principles of metal casting
- Detailed examination of sand casting methodology
- Continuous casting variants explained
- Sequential phases of sand casting production
- Technical advantages with industry data analysis
- Vendor capabilities comparison
- Customized solutions and case examples
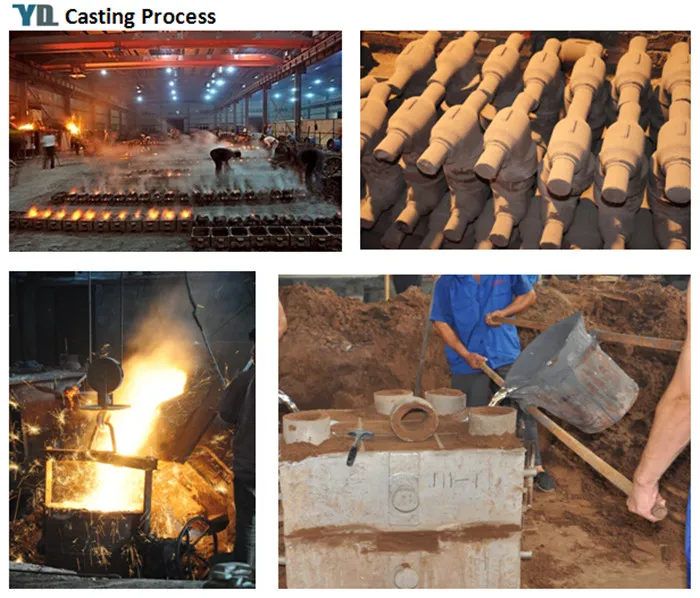

(casting process)
Understanding Metal Casting Processes
Modern manufacturing relies on metal casting process
es to create complex components across industries from automotive to aerospace. These techniques transform molten metal into predetermined shapes through mold-based solidification. Sand casting remains the most prevalent method globally, accounting for nearly 60% of all cast products manufactured. Continuous casting processes follow at 35% market penetration, providing high-volume production capabilities for standardized profiles.
Sand Foundry Methodology
Sand casting utilizes bonded silica sand molds to form intricate cavities for molten metal. This versatile method accommodates weights from 100g to 200 tons across ferrous and non-ferrous applications. Automotive cylinder blocks, pump housings, and heavy machinery components commonly emerge from sand foundries. The American Foundry Society confirms sand systems maintain 80-85% material utilization efficiency when properly managed, significantly reducing waste compared to subtractive manufacturing.
Continuous Production Varieties
Continuous casting processes include vertical, curved, and horizontal configurations depending on product specifications. Vertical systems dominate structural steel production with annual outputs exceeding 5 million metric tons per facility. Curved mold designs serve 78% of billet manufacturers while horizontal installations satisfy specialty applications requiring minimal floor space. Steel, copper, and aluminum producers leverage continuous systems for uninterrupted manufacturing with solidification rates reaching 4 meters per minute. Productivity enhancements through continuous methods generate 15-20% higher outputs versus batch processing.
Sand Casting Sequence
The sand casting process follows six systematic stages. Pattern development precedes mold preparation using compressed sand around removable templates. Gates and runners are carved before molten metal pours at precise temperatures calculated by weight-to-volume ratios (typically 760-1600°C depending on alloy). After solidification completes in 15 minutes to several hours, workers break molds and separate components. Post-processing includes runner removal, sandblasting, and dimensional verification. Final heat treatment optimizes mechanical properties for components facing operational stresses.
Technical Superiority Metrics
Modern casting delivers significant advantages over alternative manufacturing methods. Dimensional tolerances from ±0.3mm to ±5mm accommodate most engineering specifications. Production economies become evident in unit cost comparisons: CNC machining averages 200-300% higher per part costs versus casting for complex geometries. Additionally, near-net shape forming reduces material waste by 60% while maintaining mechanical properties equivalent to forged alternatives.
| Manufacturer | Casting Methods | Dimensional Tolerance | Production Volume | Material Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Castparts | Investment, Sand | ±0.3mm | 50,000 units/month | 25+ alloys |
| Alcoa Foundry | Continuous, Sand | ±0.5mm | 750 tons/month | Aluminum specialty |
| Ryobi Die Casting | Continuous, Die | ±0.25mm | 1M units/month | Zn, Mg, Al |
Custom Production Frameworks
Tailored casting solutions involve specialized design partnerships from prototype through serial production. Turbine blade manufacturers implement proprietary single-crystal solidification to optimize creep resistance. Automotive clients increasingly specify vacuum-assist sand casting to eliminate porosity in structural components. Marine sector applications employ nickel-aluminum bronzes requiring specialized cooling protocols. Production engineers adjust cooling rates between 50-300°C per minute based on metallurgical analysis of desired grain structures. Dedicated tooling investments range $10,000 for sand molds to $500,000+ for continuous casting dies.
Casting Process Implementation Results
A heavy equipment manufacturer achieved 22% cost reduction through converted sand casting production of loader arms, maintaining 1000 MPa ultimate tensile strength while shortening lead times by 40%. Energy sector implementation saw continuous casting deliver seamless pipe joints with zero failure rates after 500 pressure cycles at 150 bar. Implementation data consistently validates component lifecycle extensions between 20-35% versus traditional fabrication methods when appropriate casting solutions are employed.
(casting process)
FAQS on casting process
Q: What is the sand casting process?
A: Sand casting is a metal casting method where molten metal is poured into a sand mold. It’s widely used for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness. The mold is typically made from silica sand mixed with bonding agents.
Q: What are the types of continuous casting processes?
A: Common types include curved mold, vertical, and horizontal continuous casting. Curved mold is used for steel slabs, while horizontal suits non-ferrous metals. Each type optimizes solidification and production efficiency.
Q: What are the steps in the sand casting process?
A: Key steps are pattern creation, mold preparation, molten metal pouring, cooling, and finishing. The mold is split into cope and drag sections for easy removal. Post-casting processes include trimming and surface treatment.
Q: Which materials are commonly used in sand casting?
A: Sand casting often uses metals like iron, aluminum, bronze, and brass. The choice depends on melting point and application needs. Sand molds can withstand high temperatures of these alloys.
Q: What are the advantages of continuous casting?
A: Continuous casting ensures higher production rates and reduced material waste. It improves metal quality with uniform structure and minimizes defects. This method is ideal for mass-producing metal sheets or bars.
-
Why Should You Invest in Superior Pump Castings for Your Equipment?NewsJun.09,2025
-
Unlock Performance Potential with Stainless Impellers and Aluminum End CapsNewsJun.09,2025
-
Revolutionize Your Machinery with Superior Cast Iron and Aluminum ComponentsNewsJun.09,2025
-
Revolutionize Fluid Dynamics with Premium Pump ComponentsNewsJun.09,2025
-
Optimizing Industrial Systems with Essential Valve ComponentsNewsJun.09,2025
-
Elevate Grid Efficiency with High-Precision Power CastingsNewsJun.09,2025











