Mobile:+86-311-808-126-83
Email:info@ydcastings.com
cast moulding
Cast Moulding An Overview of the Process and Applications
Cast moulding, a fundamental technique in the manufacturing industry, involves the use of molds to create objects from various materials, primarily metals and plastics. This process allows for the production of complex shapes and components that would be difficult or impossible to achieve through traditional machining techniques.
The basic principle of cast moulding is rather straightforward. It begins with the creation of a mold, typically made from metal, sand, or ceramic materials. The mold is crafted to the desired specifications of the final product, including precise dimensions and surface finishes. Once the mold is ready, the next step is to melt the raw material—often a metal alloy or plastic resin—until it reaches a liquid state. This molten material is then poured into the mold, where it cools and solidifies to take the shape of the cavity.
One of the most significant advantages of cast moulding is its ability to produce intricate designs with high accuracy. This is particularly beneficial in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics, where components often require complex geometries for functionality and efficiency. Additionally, cast moulding can be highly efficient in terms of material use, as it minimizes waste and allows for the recycling of scrap materials.
cast moulding
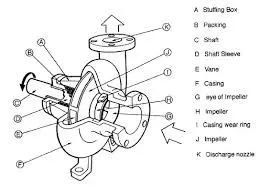
There are various methods of cast moulding, including sand casting, investment casting, and die casting, each suited for different applications and materials. Sand casting, for example, is one of the oldest and most versatile forms, employing sand as the main molding material. It is widely used for producing large parts like engine blocks and frames. In contrast, investment casting, known for its high precision and superior surface finish, is often utilized for intricate components in aerospace and medical devices.
The choice of material also plays a crucial role in cast moulding. Metals like aluminum, iron, and bronze are commonly used due to their excellent mechanical properties. On the other hand, plastics have gained popularity in cast moulding due to their lightweight and corrosion-resistant characteristics. This versatility allows manufacturers to select materials that best meet the requirements of their specific applications.
Moreover, the advancements in technology, such as computer-aided design (CAD) and 3D printing, are revolutionizing the cast moulding process. These technologies enable manufacturers to design more complex molds and streamline production, reducing lead times and costs.
In conclusion, cast moulding is a crucial manufacturing process that offers a plethora of advantages for producing complex components across various industries. As technology continues to evolve, the potential for cast moulding will expand even further, providing innovative solutions for future challenges in manufacturing.
-
Understanding Metal Casting TechniquesNewsApr.02,2025
-
Understanding Exhaust Manifolds for Enhanced Engine PerformanceNewsApr.02,2025
-
The World of Metal FabricationNewsApr.02,2025
-
Key Components for Pump and Turbo EfficiencyNewsApr.02,2025
-
Essential Tools for Automotive Maintenance and RepairNewsApr.02,2025
-
Durable Valve Components for Effective Water ManagementNewsApr.02,2025











