Mobile:+86-311-808-126-83
Email:info@ydcastings.com
suction impeller
Understanding Suction Impellers Design, Function, and Applications
Suction impellers are critical components in various fluid dynamics applications, primarily in centrifugal pumps. Their design and functionality play a significant role in determining the efficiency and performance of the pumping system. This article explores the characteristics, working principles, and applications of suction impellers, emphasizing their importance in modern engineering and industrial processes.
What is a Suction Impeller?
A suction impeller is a rotating device designed to move fluids, typically from a lower pressure area to a higher pressure area. It functions by converting mechanical energy from a motor into kinetic energy within the fluid. The impeller accelerates the fluid radially outward, creating a pressure difference that draws more fluid into the pump from the intake. This action is essential for a variety of applications, including water supply systems, wastewater treatment, and various industrial processes.
Design Characteristics
The design of suction impellers is crucial for their performance. Key factors include
1. Geometric Shape Suction impellers have specific geometric shapes, often described as open or closed. Open impellers have blades that are not fully enclosed by shrouds, which allows for easier passage of solids and is useful for handling slurries. Closed impellers, on the other hand, feature fully enclosed blades, enhancing their efficiency and ability to generate higher pressures.
2. Number of Blades The number of blades on an impeller significantly impacts its performance. Fewer blades can reduce drag but might result in lower pressure capability. Conversely, more blades can enhance efficiency but may increase drag. Striking the right balance is essential for optimal performance.
3. Material Choice The materials used in suction impeller construction must withstand the operational environment, including pressure, temperature, and fluid characteristics. Common materials include stainless steel, bronze, and various plastics, each chosen based on the specific application and fluid type.
4. Diameter and Speed The diameter of the impeller and the rotational speed dictate the flow rate and pressure that the pump can achieve. Larger diameters typically increase flow, but design must also consider the pump's overall dimensions and the motor capacity.
Working Principle
suction impeller
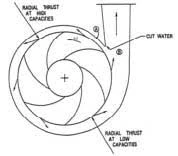
The working principle of a suction impeller is based on fluid mechanics. As the impeller spins, it creates a centrifugal force that propels the fluid outward. The fluid enters the pump at the eye (center) of the impeller, and as it flows through the blades, it gains momentum. This momentum generates a low-pressure area at the center, resulting in a pressure differential that draws more fluid into the pump from the suction line.
This process continues as long as the impeller is in motion. The efficiency of this operation greatly depends on the design of the impeller, such as the blade angle, curvature, and overall geometry, which must be optimized for the specific application.
Applications of Suction Impellers
Suction impellers find widespread use in various industries. Their applications include
1. Water Supply and Distribution In municipal water systems, suction impellers help transport potable water from treatment plants to consumers.
2. Agricultural Irrigation Suction impellers are vital in pumping systems that provide irrigation to agricultural fields, ensuring efficient water delivery.
3. Wastewater Management In wastewater treatment plants, these impellers assist in moving sewage and sludge through treatment processes, making them crucial for environmental management.
4. Industrial Processes Many manufacturing processes require the transfer of liquids, slurries, and other fluids. Suction impellers are utilized in various industries, including chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
5. Marine Applications Suction impellers are used in boats and ships for bilge pumps to circulate bilge water, ensuring the vessel remains balanced and safe.
Conclusion
In conclusion, suction impellers are indispensable in fluid handling and mechanical engineering. Their design, principles of operation, and broad applications underscore their significance in today's industrial world. Optimizing suction impeller performance can lead to significant improvements in efficiency and effectiveness, making them a focal point for engineers and designers in various sectors. Understanding their characteristics and functionalities will pave the way for advancements in pump technology and fluid dynamics applications in the future.
-
Understanding Metal Casting TechniquesNewsApr.02,2025
-
Understanding Exhaust Manifolds for Enhanced Engine PerformanceNewsApr.02,2025
-
The World of Metal FabricationNewsApr.02,2025
-
Key Components for Pump and Turbo EfficiencyNewsApr.02,2025
-
Essential Tools for Automotive Maintenance and RepairNewsApr.02,2025
-
Durable Valve Components for Effective Water ManagementNewsApr.02,2025











